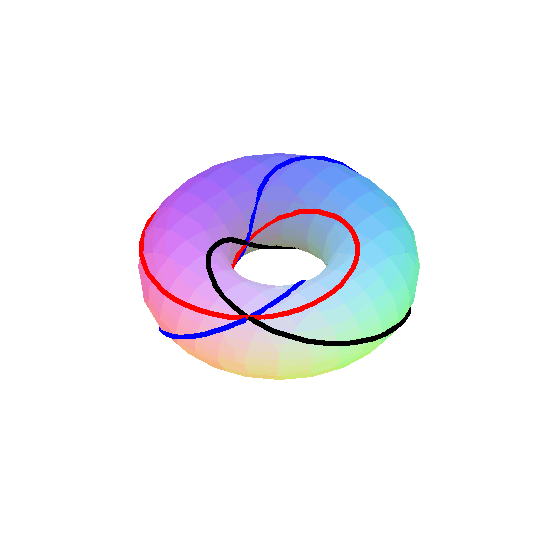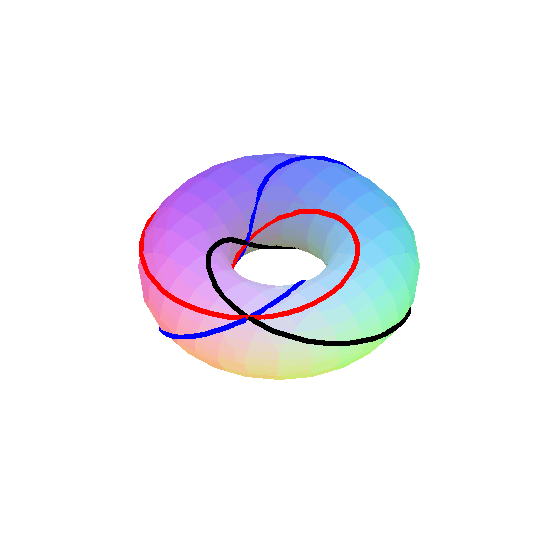
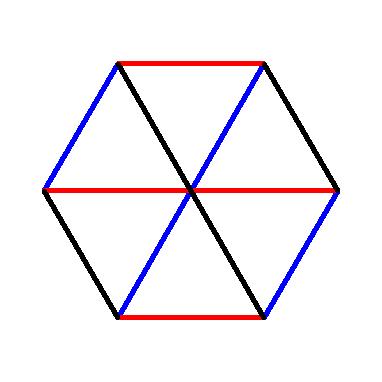
Below we see the type A2 Steinberg torus. It is formed by identifying opposite sides of a regular hexagon, where the hexagon has been cut into six equilateral triangles corresponding to the permutations of {1,2,3}.
This region is also the union of the (closure of the) alcoves neighboring the origin in affine A2.